Nobel prize winner Daniel Kahneman handed away at this time. His work incorporating psychology into economics by means of Prospect Theory has been a significant advance. From the N.Y. Times obituary:
Professor Kahneman delighted in stating and explaining what he known as common mind “kinks.” Crucial of those, the behaviorists maintain, is loss-aversion: Why, for instance, does the lack of $100 damage about twice as a lot because the gaining of $100 brings pleasure?
Amongst its myriad implications, loss-aversion concept means that IT is silly to examine one’s inventory portfolio continuously, for the reason that predominance of ache skilled within the inventory market will most certainly result in extreme and presumably self-defeating warning.
Loss-aversion additionally explains why golfers have been discovered to putt higher when going for par on a given gap than for a stroke-gaining birdie. They fight more durable on a par putt as a result of they dearly wish to keep away from a bogey, or a lack of a stroke.
For an excellent introduction of Kahneman’s contribution, one can learn the ebook Thinking, Fast and Slow. Extra technically, Prospect Principle helped to unravel a number of the key paradoxes in anticipated utility concept. From the Nobel Prize website:
Departures from the von Neumann-Morgenstern-Savage expected-utility theories of selections underneath uncertainty had been first identified by the 1988 economics laureate Maurice Allais (1953a), who established the so-called Allais paradox (see additionally Ellsberg, 1961, for a associated paradox). For instance, many people favor a sure achieve of three,000 {dollars} to a lottery giving 4,000 {dollars} with 80% chance and 0 in any other case. Nonetheless, a few of these identical people additionally favor successful 4,000 {dollars} with 20% chance to successful 3,000 {dollars} with 25% chance, despite the fact that the possibilities for the positive aspects had been scaled down by the identical issue, 0.25, in each alternate options (from 80% to twenty%, and from 100% to 25%). Such preferences violate the so-called substitution axiom of expected-utility concept…
One placing discovering is that individuals are usually far more delicate to the best way an final result differs from some non-constant reference stage (similar to the established order) than to the result measured in absolute phrases. This concentrate on modifications relatively than ranges could also be associated to well-established psychophysical legal guidelines of cognition, whereby people are extra delicate to modifications than to ranges of outdoor circumstances, similar to temperature or mild.
Furthermore, folks look like extra adversarial to losses, relative to their reference stage, than attracted by positive aspects of the identical dimension.
And a number of the mathematics behind prospect theory:
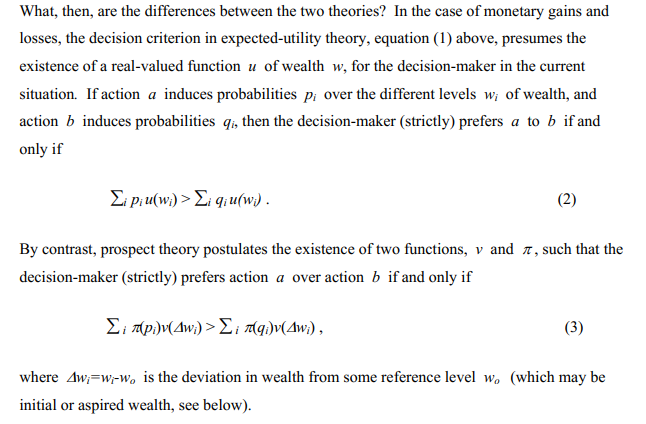
The important thing variations between anticipated utility and prospect concept: (i) anticipated utility cares about ranges whereas prospect concept evaluates modifications towards established order [i.e., w vs. Δw], (ii) prospect concept permits the utility perform and threat preferences to for positive aspects relative to losses [i.e., u(w) vs. v(w)] ], and (iii) anticipated utility concept takes chances as given whereas prospect concept makes use of determination weights which account for the way people understand these chances [i.e., p vs. π(p)].
Whereas Prospect Principle possible represents real-world human decision-making processes extra precisely than anticipated utility concept, some criticisms of Prospect Principle could be that (i) with repeated video games, people usually revert to nearer to an anticipated utility framework and (ii) for researchers, figuring out a ‘established order’ worth for every particular person is commonly difficult in observe.
Nonetheless, the Nobel Prize was a lot deserved and the scientific contributions Kahneman (and his collaborator Amos Tversky) will reside on for posterity.