We Are/DigitalVision through Getty Pictures
As I reveal my ignorance about TikTok developments, social media celebrities and Gen Z slang, my kids are fast to level out my age, and I settle for that actuality, for essentially the most half. I perceive that I’m too previous to train with out stretching first or eat a heaping plate of cheese fries and never undergo heartburn, however that doesn’t cease me from making an attempt often. For the final decade or so, I’ve argued that companies, like human beings, age, and wrestle with growing older, and that a lot of the dysfunction we observe of their decision-making stems from refusing to behave their age. In actual fact, the enterprise life cycle has develop into an integral a part of the company Finance, valuation and investing lessons that I educate, and in most of the posts that I’ve written on this weblog. In 2022, I made a decision that I had hit essential mass, in phrases of company life cycle content material, and that the fabric might be organized as a e-book. Whereas the writing for the e-book was largely carried out by November 2022, publishing does have an extended lead time, and the e-book, revealed by Penguin Random Home, might be out there on August 20, 2024, at a bookshop close to you. In case you are involved that you will be hit with a gross sales pitch for that e-book, removed from IT! Reasonably than attempt to half you out of your cash, I assumed I might give a compressed model of the e-book on this submit, and for many of you, that can suffice.
Setting the Stage
The notion of a enterprise life cycle is neither new nor authentic, since variations of IT have floated round in administration circles for many years, however its purposes in Finance have been spotty, with some makes an attempt to tie the place an organization is within the life cycle to its company governance and others to accounting ratios. In actual fact, and this could come as no shock to anybody who’s acquainted with his work, the most incisive piece tying extra returns (return on invested capital minus value of capital) to the company life cycle was penned by Michael Mauboussin (with Dan Callahan) just some months in the past.
My model of the company life cycle is constructed round six levels with the primary stage being an thought enterprise (a start-up) and the final one representing decline and demise.
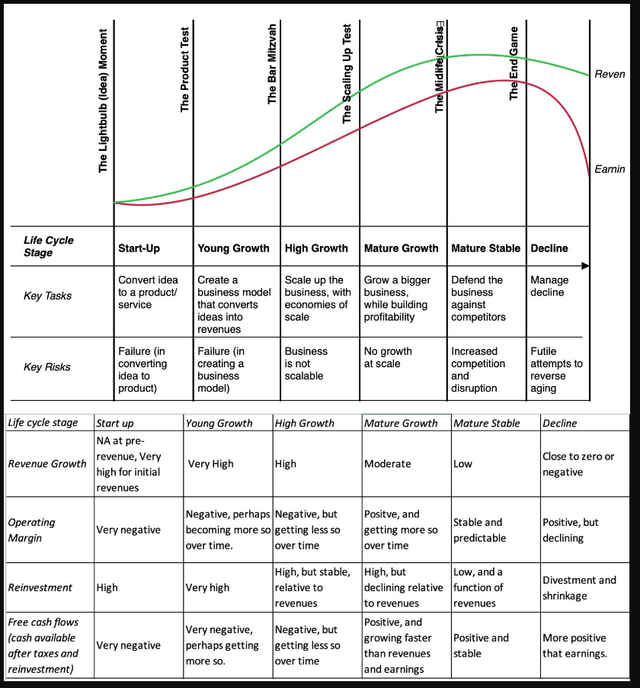
As you possibly can see, the important thing duties shift as enterprise ages, from constructing enterprise fashions within the excessive development part to scaling up the enterprise in excessive development to defending in opposition to competitors within the mature part to managing decline within the final part. Not surprisingly, the working metrics change as firms age, with excessive income development accompanied by huge losses (from work-in-progress enterprise fashions) and enormous reinvestment wants (to supply future development) in early-stage firms to massive income and free money flows within the mature part to stresses on development and margins in decline. Consequently, by way of money flows, younger firms burn by means of money, with the burn growing with potential, money buildup is widespread as firms mature adopted by money return, as the belief kicks in that an organization’s excessive development days are previously.
As firms transfer by means of the life cycle, they are going to hit transition factors in operations and in capital elevating that must be navigated, with excessive failure charges at every transition. Thus, most thought companies by no means make IT to the product part, many product firms are unable to scale up, and fairly a number of scaled up companies are unable to defend their companies from opponents. Briefly, the company life cycle has far increased mortality charges as companies age than the human life cycle, making IT crucial, if you’re a enterprise particular person, that you just discover the unusual pathways to outlive and develop.
Measures and Determinants
In the event you purchase into the notion of a company life cycle, IT stands to motive that you prefer to a strategy to decide the place an organization stands within the life cycle. There are three decisions, every with pluses and minuses.
- The primary is to give attention to company age, the place you estimate how previous an organization is, relative its founding date; IT is straightforward to acquire, however firms age at totally different charges (as nicely will argue within the following part), making IT a blunt weapon.
- The second is to take a look at the business group or sector that an organization is in, after which comply with up by classifying that business group or sector into excessive or low development; for the final 4 a long time, in US fairness markets, tech has been considered as development and utilities as mature. Right here once more, the issue is that prime development business teams start to mature, simply as firms do, and this has been true for some segments of the tech sector.
- The third is to give attention to the working metrics of the agency, with companies that ship excessive income development, with low/detrimental income and detrimental free money flows being handled as younger companies. IT is extra data-intensive, since making a judgment on what contains excessive (income development or margins) requires estimating these metrics throughout all companies.
Whereas I delve into the main points of all three measures, company age works surprisingly nicely as a proxy for the place an organization falls within the life cycle, as will be seen on this desk of all publicly traded firms listed globally, damaged down by company age into ten deciles:
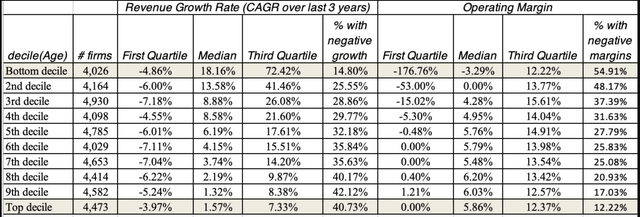
As you possibly can see, the youngest firms have a lot increased income development and extra detrimental working margins than older firms.
In the end, the life cycles for firms can fluctuate on three dimensions – size (how lengthy a enterprise lasts), top (how a lot IT can scale up earlier than IT plateaus) and slope (how shortly IT can scale up). Even a cursory look on the firms that encompass it’s best to inform you that there are broad variations throughout firms, on these dimensions. To see why, think about the elements that decide these life cycle dimensions:
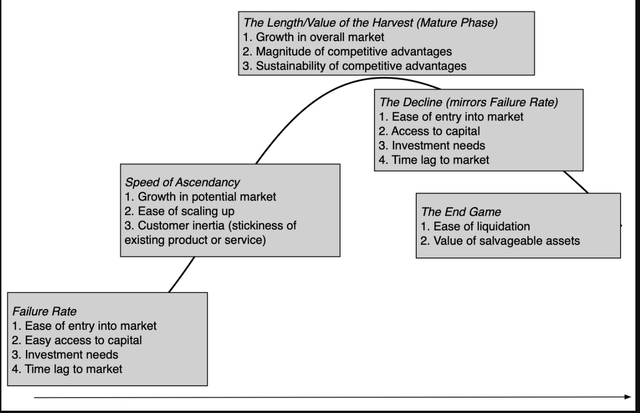
Corporations in capital-light companies, the place clients are keen to change from the established order, can scale up a lot quicker than firms in capital-intensive companies, the place model names and buyer inertia could make breakthroughs tougher. IT is value noting, although, that the forces that enable a enterprise to scale up shortly usually restrict how lengthy IT can keep on the high and trigger decline to be faster, a commerce off that was ignored over the last decade, the place scaling up was given primacy.
The drivers of the company life cycle also can clarify why the standard twenty-first century firm faces a compressed life cycle, relative to its twentieth century counterpart. Within the manufacturing-centered twentieth century, IT took a long time for firms like GE and Ford to scale up, however in addition they stayed on the high for lengthy intervals, earlier than declining over a long time. The tech-centered economic system that we reside in is dominated by firms that may scale up shortly, however they’ve transient intervals on the high and scale down simply as quick. Yahoo! and BlackBerry soared from start-ups to being value tens of billions of {dollars} in a blink of an eye fixed, had transient reigns on the high and melted all the way down to nothing nearly as shortly.
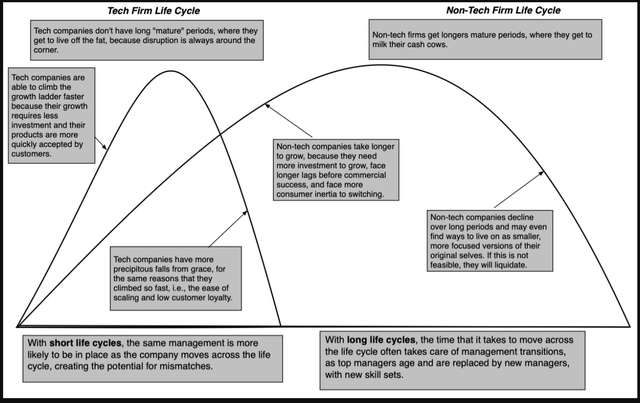
Tech firms age in canine years, and the results for the way we handle, worth and spend money on them are profound. In actual fact, I might argue that the teachings that we educate in enterprise faculty and the processes that we use in evaluation want adaptation for compressed life cycle firms, and whereas I haven’t got all of the solutions, the dialogue about altering practices is a wholesome one.
Company Finance throughout the Life Cycle
Company Finance, as a self-discipline, lays out the primary ideas that govern the best way to run a enterprise, and with a give attention to maximizing worth, all selections {that a} enterprise makes will be categorized into investing (deciding what belongings/tasks to spend money on), financing (selecting a mixture of debt and fairness, in addition to debt kind) and dividend selections (figuring out how a lot, if any, money to return to house owners, and in what type).
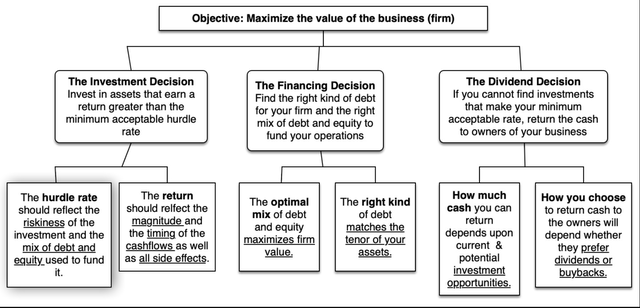
Whereas the primary ideas of company Finance don’t change as an organization ages, the main focus and estimation processes will shift, as proven within the image under:
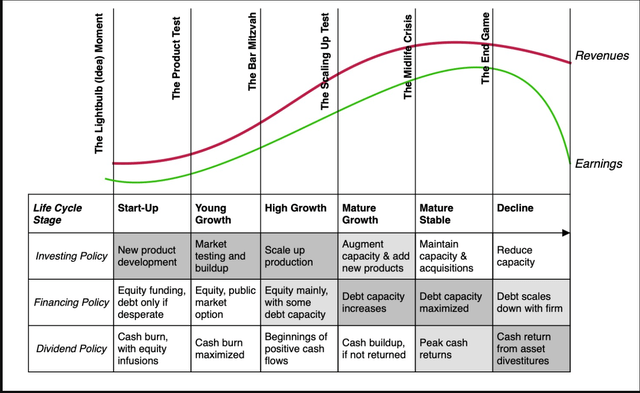
With younger firms, the place the majority of the worth lies in future development, and earnings and money flows are sometimes detrimental, IT is the funding resolution that dominates; these firms can not afford to borrow or pay dividends. With extra mature firms, as funding alternatives develop into scarcer, no less than relative to out there capital, the main focus not surprisingly shifts to financing combine, with a decrease hurdle price being the repay. With declining companies, dealing with shrinking revenues and margins, IT is money return or dividend coverage that strikes into the entrance seat.
Valuation throughout the Life Cycle
I’m fascinated by valuation, and the hyperlink between the worth of a enterprise and its fundamentals – money flows, development and danger. I’m additionally a realist and acknowledge that I reside in a world, the place pricing dominates, with what you pay for a corporation or asset being decided by what others are paying for related firms and belongings:
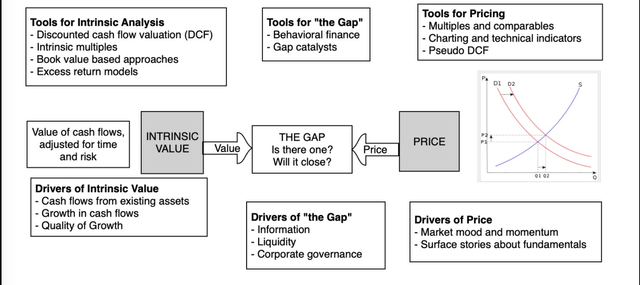
All firms will be each valued and priced, however the absence of historical past and excessive uncertainty concerning the future that characterizes younger firms makes IT extra doubtless that pricing will dominate valuation extra decisively than IT does with extra mature companies.
All companies, irrespective of the place they stand within the life cycle, will be valued, however there are key variations that may be off-putting to some. A nicely carried out valuation is a bridge between tales and numbers, with the interaction figuring out how defensible the valuation is, however the steadiness between tales and numbers will shift, as you progress by means of the life cycle:
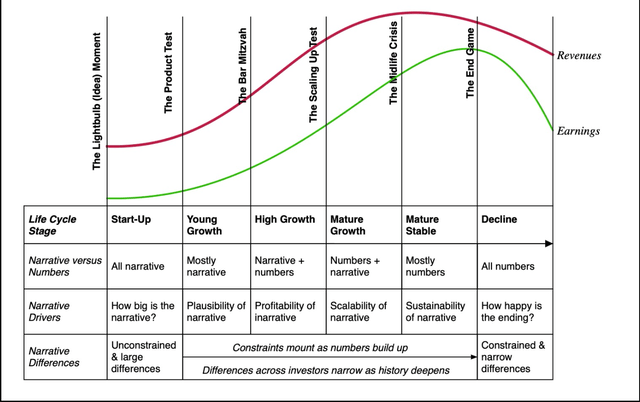
With younger firms, absent historic information on development and profitability, IT is your story for the corporate that can drive your numbers and worth. As firms age, the numbers will develop into extra essential, because the tales you inform might be constrained by what you will have been capable of ship in development and margins. In case your energy as an analyst or appraiser is in bounded story telling, you’ll be higher served valuing younger firms, whereas if you’re a number-cruncher (comfy with accounting ratios and elaborate spreadsheet fashions), you’ll find valuing mature firms to be your pure habitat.
The draw of pricing is robust even for individuals who declare to be believers in worth, and pricing in its easiest type requires a standardized value (a a number of like value earnings or enterprise worth to EBITDA) and a peer group. Whereas the pricing course of is identical for all firms, the pricing metrics you employ and the peer teams that you just examine them to will shift as firms age:
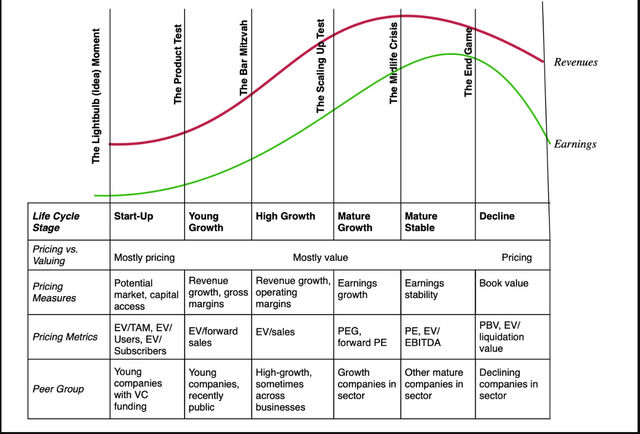
For pre-revenue and really younger firms, the pricing metrics will standardize the value paid (by enterprise capitalists and different buyers) to the variety of customers or subscribers that an organization has or to the entire market that its product is geared toward. As enterprise fashions develop, and revenues come into play, you’re more likely to see a shift to income multiples, albeit usually to estimated revenues in a future 12 months (ahead numbers). Within the mature part, you will note earnings multiples develop into extra extensively used, with fairness variations (like PE) in peer teams the place leverage is analogous throughout firms, and enterprise worth variations (EV to EBITDA) in peer teams, the place leverage is totally different throughout firms. In decline, multiples of e-book worth will develop into extra widespread, with e-book worth serving as a (poor) proxy for liquidation or break up worth. Briefly, if you wish to be open to investing in firms throughout the life cycle, IT behooves you to develop into comfy with totally different pricing ratios, since nobody pricing a number of will work on all companies.
Investing throughout the Life Cycle
In my class (and e-book) on funding philosophies, I begin by noting that each funding philosophy is rooted in a perception about markets making (and correcting) errors, and that there isn’t any one greatest philosophy for all buyers. I exploit the funding course of, beginning with asset allocation, transferring to inventory/asset choice and ending with execution to indicate the vary of views that buyers convey to the sport:
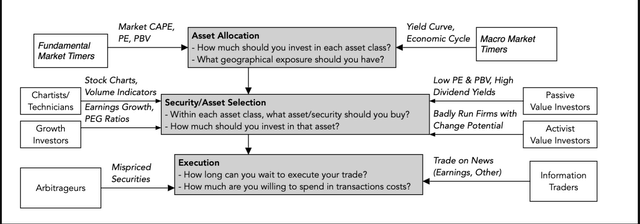
Market timing, whether or not IT be primarily based on charts/technical indicators or fundamentals, is primarily targeted on the asset allocation part of investing, with cheaper (primarily based upon your market timing measures) asset lessons being over weighted and dearer asset lessons being underneath weighted. Inside the inventory choice part, there are an entire host of funding philosophies, usually holding contradictory views of market conduct. Amongst inventory merchants, as an example, there are those that consider that markets be taught slowly (and go along with momentum) and those that consider that markets overreact (and wager on reversals). On the investing aspect, you will have the traditional divide between worth and development buyers, each claiming the excessive floor. I view the variations between these two teams by means of the prism of a monetary steadiness sheet:
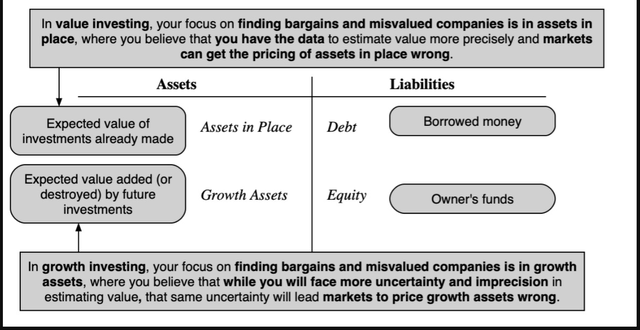
Worth buyers consider that the very best funding bargains are in mature firms, the place belongings in place (investments already made) are being underpriced by the market, whereas development buyers construct their funding theses round the concept IT is development belongings the place markets make errors. Lastly, there are market gamers who attempt to earn cash from market frictions, by locking in market mispricing (with pure or close to arbitrage).
Drawing on the sooner dialogue of worth versus value, you possibly can classify market gamers into buyers (who worth firms, and attempt to purchase them at a lower cost, whereas hoping that the hole closes) and merchants (who make them cash on the pricing sport, shopping for at a low value and promoting at the next one). Whereas buyers and merchants are a part of the market in each firm, you’re more likely to see the steadiness between the 2 teams shift as firms transfer by means of the life cycle:
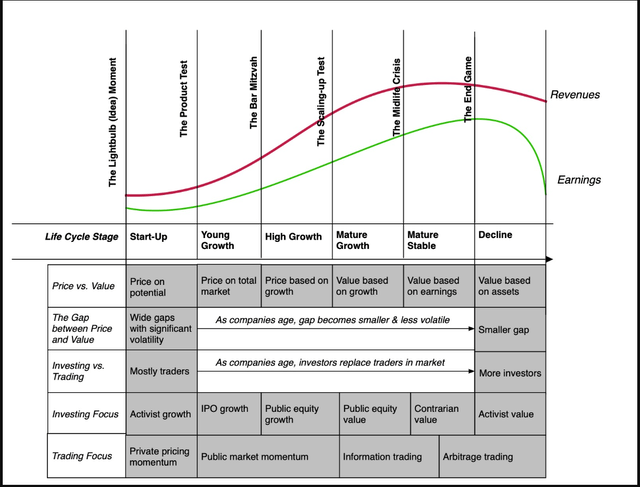
Early within the life cycle, IT is simple that merchants dominate, and for buyers in these firms, even when they’re proper of their worth assessments, profitable would require for much longer time horizons and stronger stomachs. As firms mature, you’re more likely to see extra buyers develop into a part of the sport, with discount hunters coming into when the inventory drops an excessive amount of and brief sellers extra keen to counter when IT goes up an excessive amount of. In decline, as authorized and restructuring challenges mount, and an organization can have a number of securities (convertibles, bonds, warrants) buying and selling on IT, hedge funds and activists develop into greater gamers.
In sum, the funding philosophy you select can lead you to over spend money on firms in some phases of the life cycle, and whereas that by itself just isn’t an issue, denying that this skew exists can develop into one. Thus, deep worth investing, the place you purchase shares that commerce at low multiples of earnings and e-book worth, will end in bigger parts of the portfolio being invested in mature and declining firms. That portfolio will benefit from stability, however anticipating IT to comprise ten-baggers and hundred-baggers is a attain. In distinction, a enterprise capital portfolio, invested nearly completely in very younger firms, can have numerous wipeouts, however IT can nonetheless outperform, if IT has a number of massive winners. Recommendation on concentrating your portfolio and having a margin of security, each worth investing nostrums, may go with the previous however not with the latter.
Managing throughout the Life Cycle
Administration consultants who educate at enterprise faculties and populate the premier consulting companies have a lot to realize by propagating the parable that there’s a prototype for a great CEO. In spite of everything, IT provides them a motive to cost nose-bleed costs for an MBA (to be imbued with these qualities) or for consulting recommendation, with the identical finish sport. The reality is that there isn’t any one-size-fits-all for an important CEO, because the qualities that you’re searching for in high administration will shift as firms age:
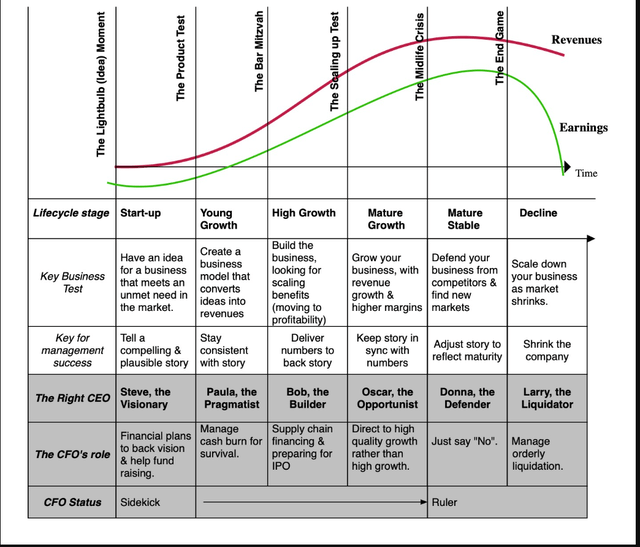
Early within the life cycle, you need a visionary on the high, since you need to get buyers, staff and potential clients to purchase into that imaginative and prescient. To show the imaginative and prescient into services and products, although, you want a pragmatist, keen to just accept compromises. As the main focus shifts to enterprise fashions, IT is the business-building expertise that make for an important CEO, permitting for scaling up and success. As a scaled-up enterprise, the talent units change once more, with opportunism turning into the important thing high quality, permitting the corporate to seek out new markets to develop in. In maturity, the place enjoying protection turns into central, you need a high supervisor who can guard an organization’s aggressive benefits fiercely. Lastly, in decline, you need CEOs, unencumbered by ego or the will to construct empires, who’re keen to preside over a shrinking enterprise, with divestitures and money returns excessive on the to-do record.
There are only a few individuals who have all of those expertise, and IT ought to come as no shock that there could be a mismatch between an organization and its CEO, both as a result of they (CEO and firm) age at totally different charges or due to hiring errors. These mismatches will be catastrophic, if a headstrong CEO pushes forward with actions which might be unsuited to the corporate she or he is in cost off, however they are often benign, if the mismatched CEO can discover a companion who can fill in for weaknesses:

Whereas the probabilities of mismatches have all the time been a part of enterprise, the compression of company life cycles has made them each more likely, in addition to extra damaging. In spite of everything, time took care of administration transitions for long-lived twentieth century companies, however with companies that may scale as much as develop into market cap giants in a decade, earlier than cutting down and disappearing within the subsequent one, you possibly can very nicely see a founder/CEO go from being a hero in a single part to a zero within the subsequent one. As we now have allowed most of the most profitable companies which have gone public on this century to skew the company Finance sport, with shares with totally different voting rights, we could also be shedding our energy to alter administration at these companies the place the necessity for change is biggest.
Growing old gracefully?
The healthiest response to growing older is acceptance, the place a enterprise accepts the place IT is within the life cycle and behaves accordingly. Thus, a younger agency that derives a lot of its worth from future development mustn’t put that in danger by borrowing cash or by shopping for again inventory, simply as a mature agency, the place worth comes from its current belongings and aggressive benefits, mustn’t danger that worth by buying firms in new and unfamiliar companies, in an try to return to its development days. Acceptance is most tough for declining companies, because the administration and buyers must make peace with downsizing the agency. For these companies, IT is value emphasizing that acceptance doesn’t suggest passivity, a distorted and defeatist view of karma, the place you do nothing within the face of decline, however requires actions that enable the agency to navigate the method with the least ache and most worth to its stakeholders.
IT ought to come as no shock that many companies, particularly in decline, select denial, the place managers and buyers give you excuses for poor efficiency and lay blame on outdoors elements. On this path, declining companies will proceed to behave the best way they did once they had been mature and even development firms, with massive prices to everybody concerned. When the promised turnaround doesn’t ensue, desperation turns into the choice path, with managers playing massive sums of different individuals’s cash on lengthy pictures, with predictable outcomes.
The siren music that attracts declining companies to make these makes an attempt to recreate themselves, is the hope of a rebirth, and an ecosystem of bankers and consultants presents them magic potions (taking the type of proprietary acronyms that both restate the plain or are constructed on foundations of made-up information) that can make them younger once more. They’re aided and abetted by case research of firms that discovered pathways to reincarnation (IBM in 1992, Apple in 2000 and Microsoft in 2013), with the added bonus that their CEOs had been elevated to legendary standing. Whereas IT is simple that firms do typically reincarnate, IT is value recognizing that they continue to be the exception somewhat than the rule, and whereas their high administration deserves plaudits, luck performed a key function as nicely.
I’m a skeptic on sustainability, no less than as utilized to firms, since IT makes company survival the top sport, typically with substantial prices for a lot of stakeholders, in addition to for society. Just like the Egyptian Pharaohs who sought immortality by wrapping their our bodies in bandages and being buried with their favourite possessions, firms that search to reside eternally will develop into mummies (and typically zombies), sucking up assets that might be higher used elsewhere.
In conclusion
IT is the dream, in each self-discipline, to give you a principle or assemble that explains every thing in that disciple. Not like the bodily sciences, the place that search is constrained by the legal guidelines of nature, the social sciences replicate extra trial and error, with the unpredictability of human nature being the wild card. In Finance, a self-discipline that began as an offshoot of economics within the Fifties, that search started with theory-based fashions, with portfolio principle and the CAPM, veered into data-based constructs (proxy fashions, issue evaluation), and behavioral Finance, with its marriage of Finance and psychology. I’m grateful for these contributions, however the company life cycle has supplied me a low-tech, however surprisingly wide-reaching, assemble to clarify a lot of what I see in enterprise and funding conduct.
If you end up within the matter, you possibly can strive the e-book, and within the pursuits of creating IT accessible to a various reader base, I’ve tried to make IT each modular and self-standing. Thus, if you’re keen on how operating the enterprise adjustments, as IT ages, you possibly can give attention to the 4 chapters that take a look at company Finance implications, with the lead-in chapter offering you adequate of a company Finance basis (even when you’ve got by no means taken a company Finance class) to have the ability to perceive the investing, financing and dividend results. In case you are an appraiser or analyst, keen on valuing firms throughout the life cycle, IT is the 5 chapters on valuation which will draw your curiosity, once more with a lead-in chapter containing an introduction to valuation and pricing. As an investor, it doesn’t matter what your funding philosophy, IT is the 4 chapters on investing throughout the life cycle which will enchantment to you essentially the most. Whereas I’m positive that you’ll have no hassle discovering the e-book, I’ve an inventory of e-book retailers listed under that you need to use, should you select, and the webpage supporting the book can be found here.
E-book and Class Webpages
- E-book webpage: Little Book of Valuation
- Class webpage: Webcasts: Investment Philosophies
- YouTube Playlist for sophistication.
Hyperlinks to booksellers
- Amazon: The Corporate Life Cycle: Business, Investment, and Management Implications
- Barnes & Noble: The Corporate Life Cycle: Business, Investment, and Management Implications|Hardcover
- Bookshop.org: The Corporate Life Cycle: Business, Investment, and Management Implications
- Apple: The Corporate Life Cycle: Business, Investment, and Management Implications (Unabridged)
Editor’s Observe: The abstract bullets for this text had been chosen by Looking for Alpha editors.
👇Observe extra 👇
👉 bdphone.com
👉 ultraactivation.com
👉 trainingreferral.com
👉 shaplafood.com
👉 bangladeshi.help
👉 www.forexdhaka.com
👉 uncommunication.com
👉 ultra-sim.com
👉 forexdhaka.com
👉 ultrafxfund.com
👉 ultractivation.com
👉 bdphoneonline.com
👉 Subscribe us on Youtube